Identification of Collared Laughingthrush
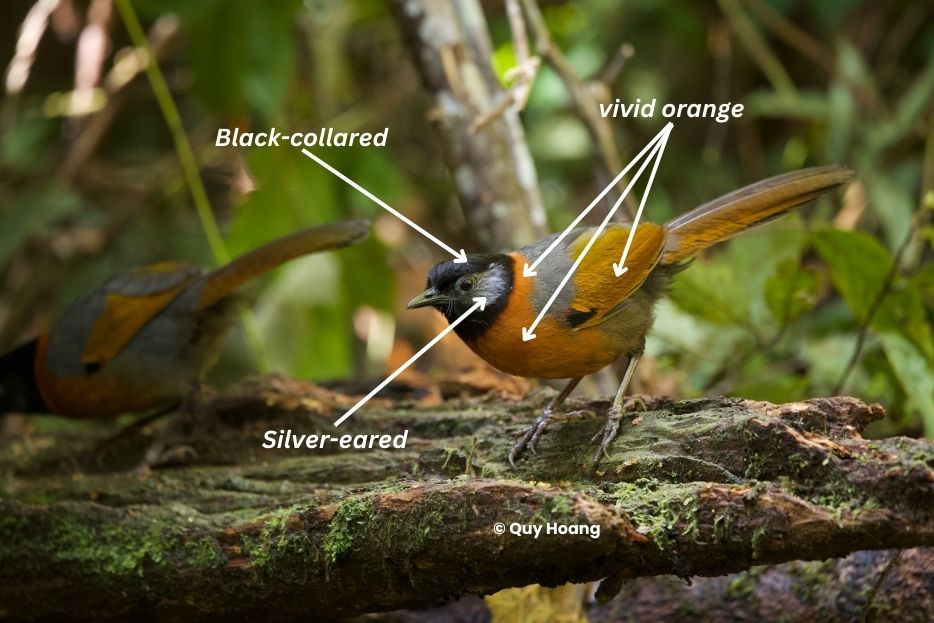
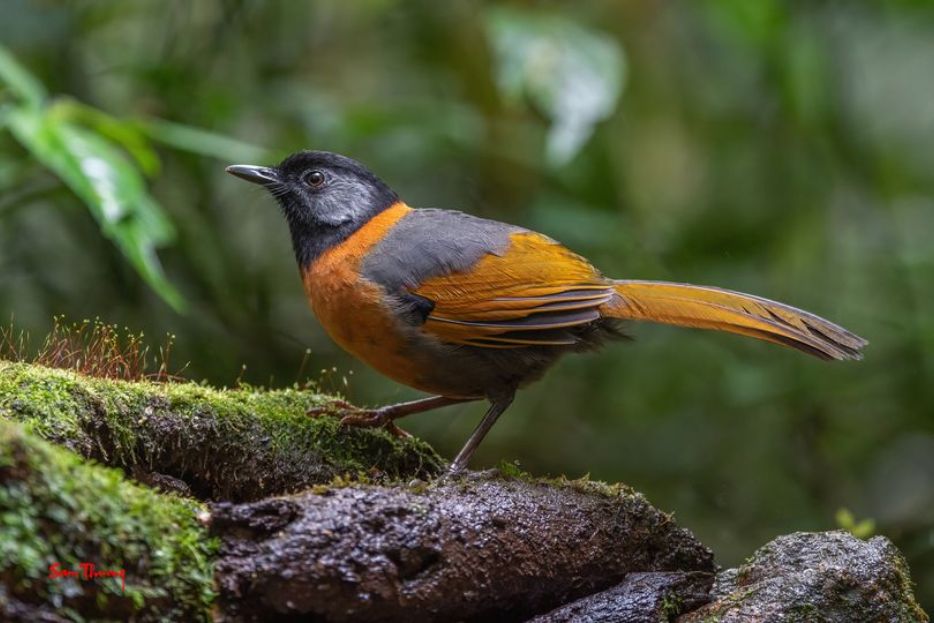
The Collared Laughingthrush is a striking and unmistakable bird, known for its unique and vibrant Halloween-themed plumage. This species is adorned in a dramatic combination of black, gray, and orange. Its head is entirely black, which contrasts sharply with the silver patch on its ear-coverts, creating a striking facial appearance. The bird’s neck and upper breast are a vivid orange, which extends to its upper belly and forms a distinct “collar” around its body. The wings are multicolored, featuring olive-yellow with black wing coverts and tail feathers. The bird’s tail is olive-brown with yellow edges, while the rest of its body is primarily gray. Its underbelly and undertail coverts are olive-brown, completing its unique and eye-catching appearance.

Distinctive Features
The Collared Laughingthrush’s distinctive black head, silver ear patch, and orange neck and breast make it easily recognizable within its range. Its color pattern is bizarrely reminiscent of much smaller species like the Silver-eared Mesia and Golden-breasted Fulvetta, despite being significantly larger. The striking contrast of colors and the bird’s overall appearance set it apart from other laughingthrushes, ensuring it is not easily confused with other species in its habitat.
Check more detail of Collared Laughingthrush here
Habitat Preferences
The Collared Laughingthrush inhabits mid- to high-altitude forests, typically between 1,400 to 2,440 meters above sea level. It is primarily found under the canopy of evergreen broadleaf forests or coniferous forests in high mountains. This species prefers dense understory vegetation, where it rummages around in small groups. In Vietnam, its distribution is limited to specific regions such as the Chư Yang Sin Nature Reserve in Đắk Lắk and areas in Lâm Đồng, including the Đà Lạt Plateau. These habitats provide the dense cover and the specific altitudinal range that the species requires.
Behavioral Traits
The Collared Laughingthrush is often observed foraging in the understory of its forested habitat, usually in small groups. Despite its striking appearance, it can be elusive, blending well with the dense vegetation it inhabits. The bird is known for its odd, rising, and screaming yodel-like call, which is strangely reminiscent of the call of an Indian Peafowl. This distinctive vocalization can be a key indicator of its presence in the wild, especially when visual sightings are challenging.
Challenges and Conservation Status
The Collared Laughingthrush is currently classified as Endangered due to its very small and severely fragmented range. The species is endemic to Vietnam, and its population is estimated to be between 2,500 to 9,999 mature individuals. The primary threats to its survival include forest degradation and fragmentation, which are causing a continued decline in both its population and habitat quality. The extent of occurrence for the breeding and resident populations is estimated to be around 2,700 square kilometers. The bird’s status is a significant concern, as it is not common within its limited distribution range.

How to Look for It
To successfully observe the Collared Laughingthrush, birdwatchers should focus on high-elevation forests in Vietnam, particularly within the Chư Yang Sin Nature Reserve and the Đà Lạt Plateau. The bird is most active in the understory, so it is essential to scan dense vegetation carefully. Early mornings are the best times to search for this species, as it is more likely to be foraging or vocalizing during these hours. Listening for its distinctive yodel-like call can also help locate it, especially since the bird is known to be elusive and well-camouflaged in its natural habitat.
Best Seasons to Spot
The Collared Laughingthrush can be observed year-round within its range, but the best chances to spot it are during the dry season, which typically extends from December to April. During this time, the weather is more favorable for birdwatching, and the birds tend to be more active and vocal. Late April to early May might be less ideal as the birds become quieter, making them harder to detect.
Top 4 Locations to Spot the Collared Laughingthrush
Chư Yang Sin Nature Reserve, Đắk Lắk:
Specific Areas/Trails: Focus on mid- to high-elevation areas within the reserve, particularly above 2,000 meters, where dense evergreen forests provide the necessary cover.
Best Times for Observation: Early morning hours are the most productive, though sightings can be challenging due to the bird’s secretive nature.
Challenges: The rugged terrain and dense vegetation make spotting the Collared Laughingthrush difficult. Patience and familiarity with its call are crucial.
Đà Lạt Plateau, Lâm Đồng:
- Specific Areas/Trails: Target areas within the plateau’s evergreen forests, especially those with a thick understory at higher elevations.
- Best Times for Observation: Like in Chư Yang Sin, early mornings are the best time for sightings.
- Challenges: The limited range and fragmented habitat make this bird one of the more difficult species to observe in the region.
Bidoup-Nui Ba National Park:
- Best Place in Vietnam: Bidoup-Nui Ba National Park is renowned as the best place in Vietnam to encounter the Collared Laughingthrush. The park is equipped with a specially designed hide that provides a very high chance of observing this species up close. The hide is strategically located within the bird’s preferred habitat, offering optimal conditions for sightings.
- Specific Areas/Trails: The hide is positioned in an area with dense understory vegetation at higher elevations, where the Collared Laughingthrush is known to forage and vocalize.
- Best Times for Observation: Early morning hours provide the best opportunity to see the bird as it becomes active at dawn. The hide allows for extended observation periods without disturbing the birds, increasing the likelihood of a successful sighting.
- Challenges: While the hide significantly enhances the chances of spotting the species, the Collared Laughingthrush remains elusive, so patience and a quiet approach are essential.
4. Giang Ly and Hon Giao Mountain:
- Largest Population: Giang Ly and Hon Giao Mountain host the largest number of Collared Laughingthrush individuals in Vietnam, making these areas prime locations for encountering the species.
- Specific Areas/Trails: These locations feature extensive tracts of evergreen forests with dense understory, situated at elevations ideal for the Collared Laughingthrush. The terrain here offers excellent conditions for both foraging and nesting, which contributes to the high density of individuals.
- Best Times for Observation: Similar to Bidoup-Nui Ba, the best time to visit Giang Ly and Hon Giao is early morning when the birds are most active. Their distinctive calls can often be heard echoing through the forest, guiding birdwatchers to their location.
- Challenges: The rugged terrain and dense forest can make access challenging. However, the large population in these areas increases the chances of sightings, making the effort worthwhile.
Tour include chance to see Collared Laughingthrush
See below or click to go straight
Crocodile Trail – The Best Birding Trail in Cat Tien National Park
If you’re a birder or nature photographer planning a trip to Vietnam, few places offer [...]
Cong Troi Trail – Top 1 Dalat Plateau Birding Trail Experience
If you’re a birder or nature photographer planning a trip to Vietnam’s Central Highlands, the [...]
How to Identify the Greater Sand Plover, Tibetan Sand Plover and Siberian Sand Plover
ContentsIdentification of Collared LaughingthrushTop 4 Locations to Spot the Collared LaughingthrushTour include chance to see [...]
Highlights of Cat Tien National Park Reptiles and Amphibian Endemics
Spanning over 71,350 hectares of tropical forests, grasslands, and wetlands, Cat Tien National Park is [...]
Highlights of Cat Tien National Park Mammals in a World Biosphere Reserve
In addition to reptiles and birds, Cat Tien National Park is also rich in mammals, [...]
Kontum Plateau Endemic and Highlight bird
Kontum Plateau Endemic And Highlight Bird species like Chestnut-eared Laughingthrush and top birding routes while [...]